Research
You can find a full list of my publications on NASA ADS here.
Supernovae in redMaGiC galaxies
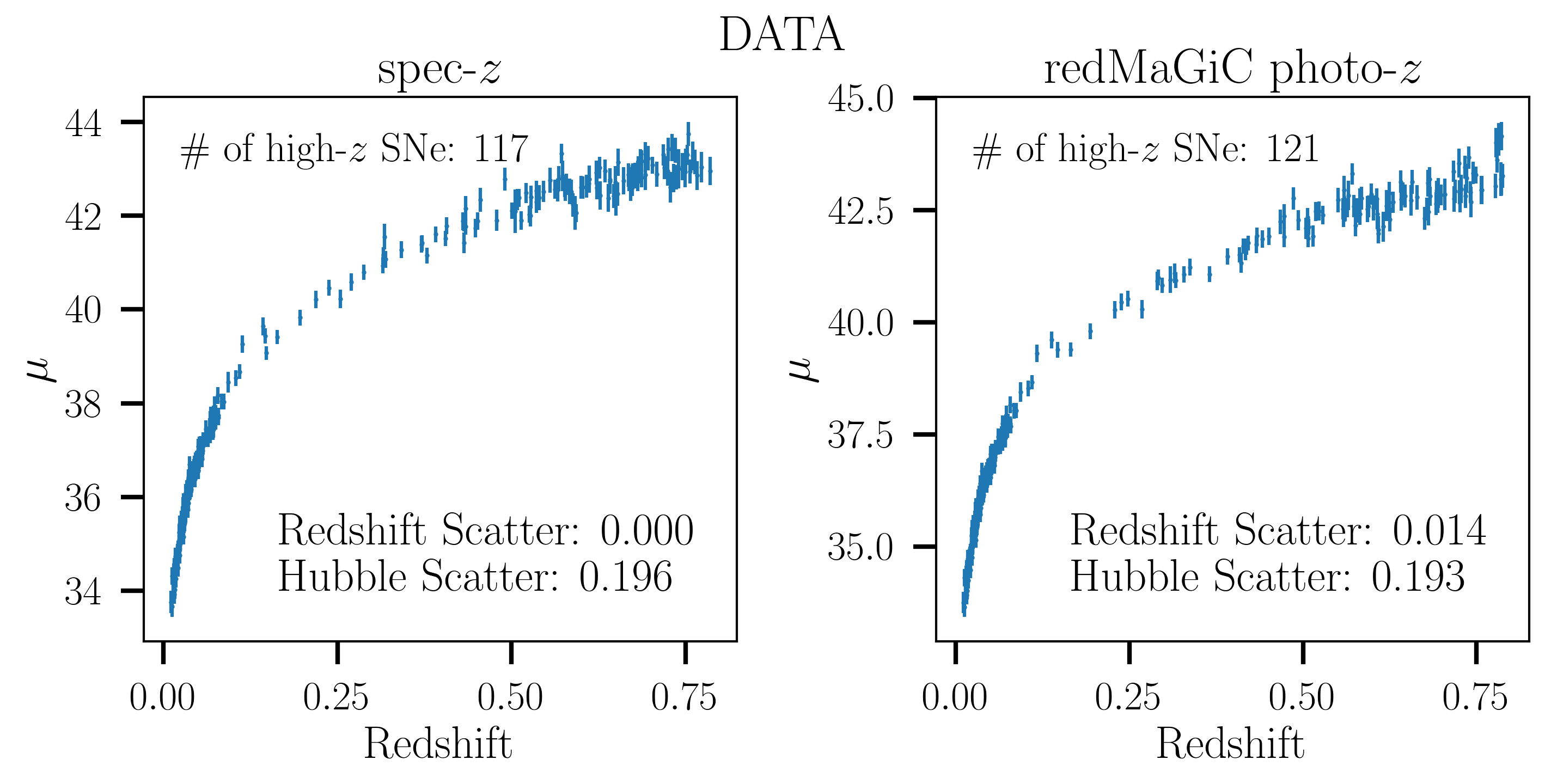
Cosmological analyses with Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) typically rely heavily on spectroscopy to both classify the type of the supernova and obtain redshifts from either the supernova or its host galaxy. Upcoming photometric surveys such as LSST and Roman will observe more than a million SNe (compared to the ~1800 in our current largest compilations), for which obtaining spectroscopy for every event is unfeasible. I have worked on a novel approach to this problem, which focuses on DES SNe Ia hosted in redMaGiC galaxies, a selection of Luminous Red Galaxies that has traditionally been used in large-scale structure studies. redMaGiC galaxies are selected to have minimal photometric redshift (photo-z) estimate uncertainties and are expected to have very low rates of core-collapse supernovae. The subset of SNe in LRGs also presents a unique opportunity to better understand the relationship between host-galaxy properties and SN light properties, as LRGs are passive and nearly dust-free. In my 2022 paper, we present the method and results of this first proof-of-concept analysis that lays the groundwork for the use of photometric redshifts for SNe Ia cosmology.
SN+Host-galaxy photometric redshifts for Ia Cosmology
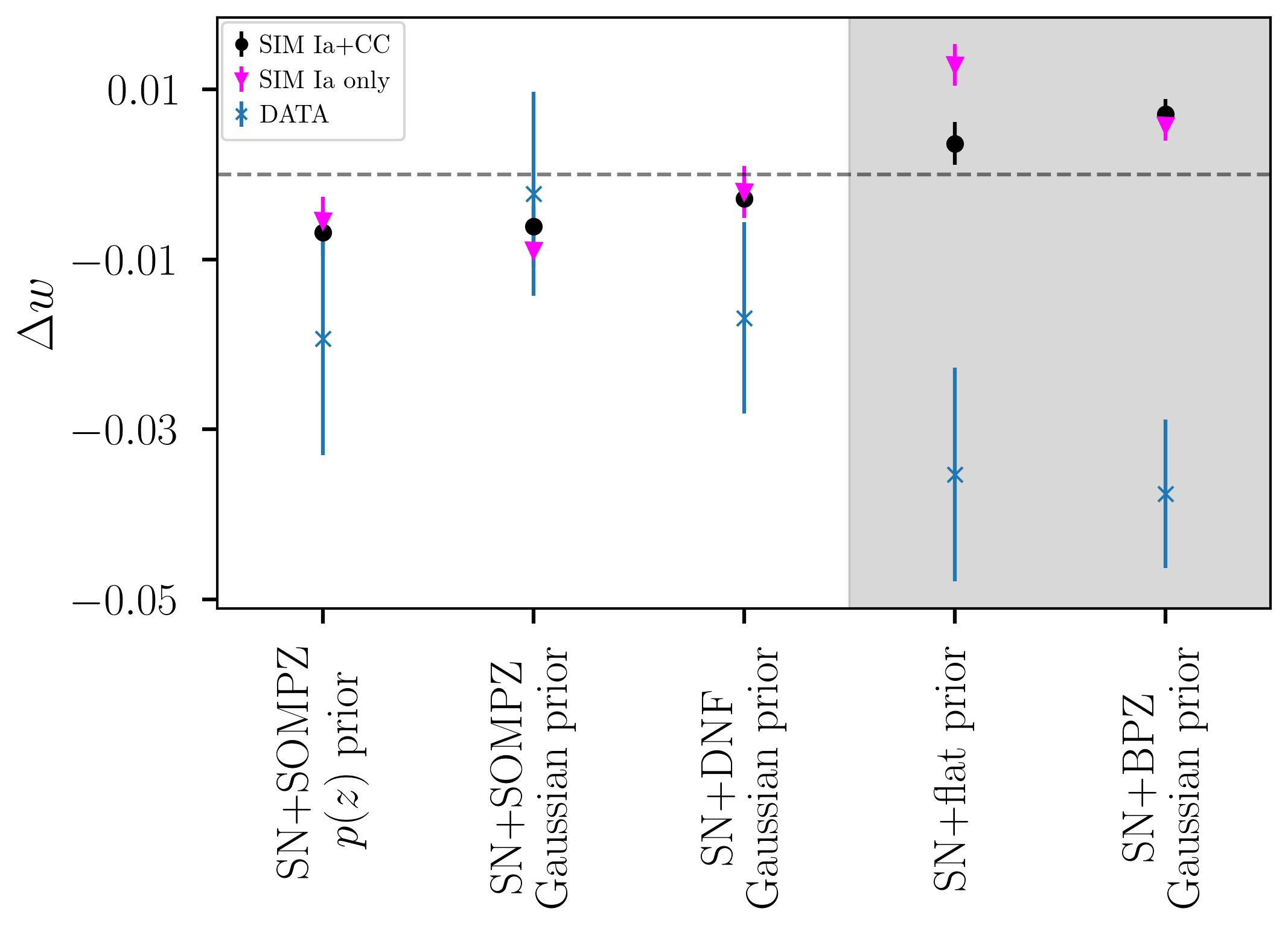
My most recent paper evaluates the cosmological biases that can occur when we use photometric redshifts from all types of galaxies, not just those with particularly good photo-z. Using the DES5YR photometrically classified sample, we focus on photo-z estimated from the SN light-curve with a prior from several machine learning and template fitting host galaxy photometric redshift algorithms (SOMPZ, DNF, BPZ) used in the DES 3x2 pt analyses. We also include a full treatment of core-collapse contamination and include a dust-based intrinsic scatter model. We validate these results with detailed catalog-level simulations and find biases in w ~0.02 that are consistently subdominant to the statistical uncertainty. This is a big step forward to showing that we can do a fully photometric (photometric classification AND photometric redshifts) analysis with the upcoming LSST and Roman surveys.
Roman grism redshift recovery efficiency for SNIa host galaxies
Results incoming – paper in prep.
